Lewis Acid-catalyzed Selective [2+2]-Cycloaddition and Dearomatizing Cascade Reaction of Aryl Alkynes with Acrylates
Liang Shen,aKai Zhao,a,bKazuki Doitomi,cRakesh Ganguly,aYong-Xin Li,aZhi-Liang Shen,*,a,bHajime Hirao,b,cand Teck-Peng Loh*,a,b
aInstitute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, P. R. China 210009.
bDivision of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371
cDepartment of Chemistry, City University of Hong Kong, Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
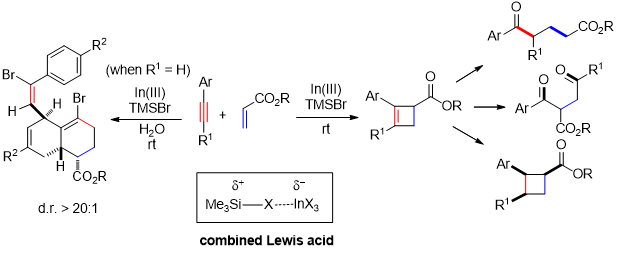
Abstract:Combined Lewis acid, consisting of two or more Lewis acids, sometimes shows unique catalytic ability and it may promote reactions which could not be catalyzed by any of the Lewis acid solely. On the other hand, the development of efficient methods for the facile synthesis of cyclobutenes and densely functionalized decalins are attractive targets for synthetic chemists due to their versatile synthetic utilities and widespread occurrence in natural products. Herein we wish to report an efficient method for the assembly of cyclobutenes and densely functionalized decalin skeletons through In(tfacac)3-TMSBr catalyzed selective [2+2]-cycloaddition and dearomatizing cascade reaction of aryl alkynes with acrylates with high chemo- and stereoselectivity. The obtained cyclobutene could be easily converted into cyclobutane as well as synthetically useful 1,4- and 1,5-diketones with high chemo- and stereoselectivity. Based on mechanistic studies, plausible reaction mechanisms were proposed for both of the [2+2]-cycloaddition and the dearomatizing cascade reaction. Finally, the computational studies of reaction mechanisms were conducted and the results suggest that the combined Lewis acid could efficiently promote both reactions.
Journal of the American Chemical Society2017,139, 13570-13578; (2017 Impact factor: 13.858).
