One-pot Aminobenzylation of Aldehydes with Toluenes
Zhiting Wang1, Zhipeng Zheng2, Xinyu Xu1, Jianyou Mao1& Patrick J. Walsh1,2
1Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, 30 South Puzhu Road, 211816 Nanjing, China.
2Roy and Diana Vagelos Laboratories, Penn/Merck Laboratory for High-Throughput Experimentation, Department of Chemistry, University of Pennsylvania, 231 South 34th Street, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.
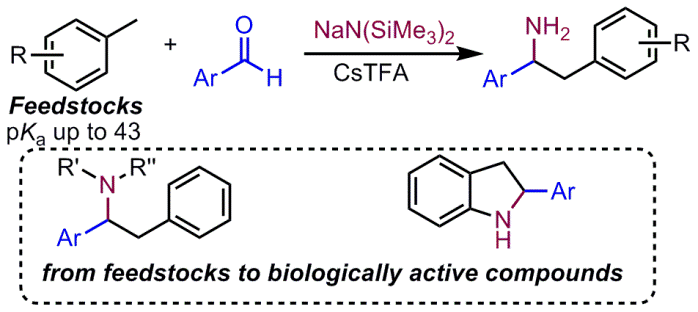
Abstract:Amines are fundamental motifs in bioactive natural products and pharmaceuticals. Using simple toluene derivatives, a one-pot aminobenzylation of aldehydes is introduced that provides rapid access to amines. Simply combining benzaldehydes, toluenes, NaN(SiMe3)2, and additive Cs(O2CCF3) (0.35 equiv.) generates a diverse array of 1,2-diarylethylamine derivatives (36 examples, 56–98% yield). Furthermore, suitably functionalized 1,2-diarylethylamines were transformed into 2-aryl-substituted indoline derivatives via Buchwald–Hartwig amination. It is proposed that the successful deprotonation of toluene by MN(SiMe3)2 is facilitated by cation–π interactions between the arene and the group(I) cation that acidify the benzylic C–Hs.
Nature Communications (2018), 9(1), 1-8. (2018年影响因子: 12.353第一作者为硕士研究生王志婷).
论文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05638-y
